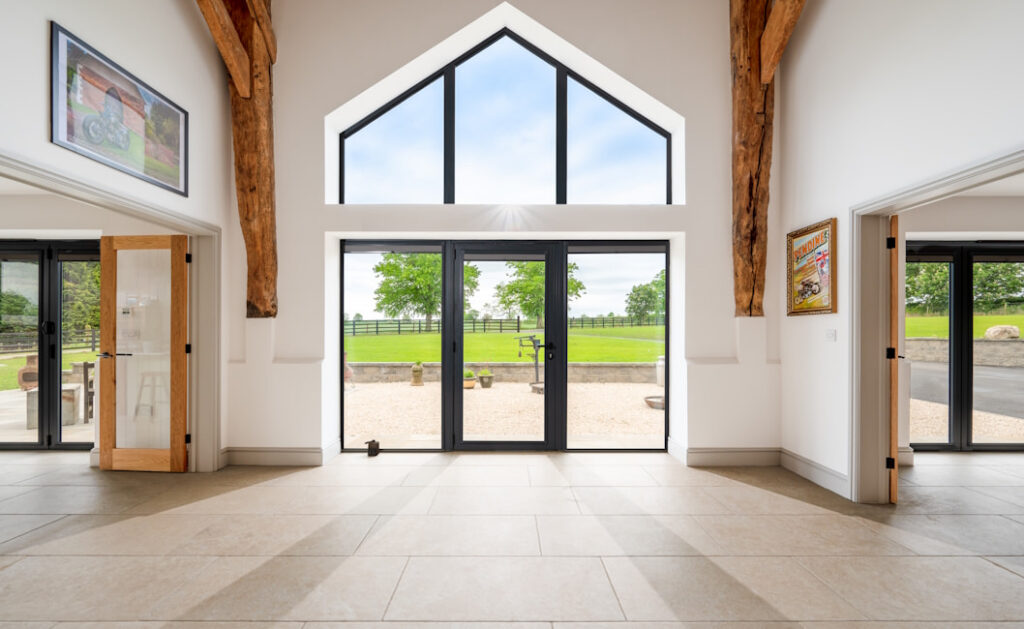

A window installed within a gable the triangular upper part of a wall formed by a pitched roof is a distinctive architectural feature. These windows provide natural light and ventilation to attic spaces or rooms located directly beneath the roofline. An example includes a rectangular pane set high within the triangular space of a steeply pitched roof, offering illumination to the upper story.
The placement of such a window allows for increased natural light penetration into otherwise dimly lit areas. This can enhance the aesthetic appeal of a structure’s interior while reducing reliance on artificial lighting. Historically, these architectural elements have served as functional necessities in homes and structures, offering ventilation and light, while also contributing to the building’s overall character and style. Their presence can denote a specific architectural period or design philosophy.
Understanding the specific applications, design considerations, and structural implications of this architectural feature is crucial for informed building design and renovation projects. Subsequent sections will explore various aspects of these window designs, including their types, installation, and maintenance.
1. Shape and Size
The shape and size of a gable window are critical design parameters impacting both the aesthetic and functional aspects of a building. The triangular form of the gable end inherently influences the available area for window placement, directly dictating the maximum dimensions achievable. A larger window, predicated on suitable gable wall area, permits greater natural light infiltration, thereby reducing the need for artificial illumination. Conversely, undersized windows may prove inadequate, diminishing the intended benefit. Rectangular, arched, or even custom-shaped windows are common within gable ends; however, the geometry of the gable dictates the feasible options and necessitates careful consideration of structural load-bearing capacity. A poorly sized or shaped window can compromise the structural integrity of the gable wall, particularly in regions prone to high winds or seismic activity.
For example, consider a renovated farmhouse. The original gable end may have accommodated a small, square window. Modern renovation plans frequently call for larger, more elaborate window designs to enhance the interior ambiance. Implementing such a change necessitates a thorough structural analysis to determine if the existing gable structure can support the increased load and altered weight distribution. The shape also influences the perceived architectural style. A Gothic arch shape might suit Victorian architecture, while a simple rectangle window fits modern home design. Neglecting this consideration can lead to a jarring visual mismatch.
Ultimately, the selection of appropriate shape and size for a gable window necessitates a comprehensive understanding of structural limitations, architectural design principles, and functional requirements. Ignoring these factors can result in compromised structural integrity, inadequate illumination, and diminished aesthetic appeal. Therefore, consultation with structural engineers and experienced architects is crucial to ensure the successful integration of gable windows into any building project, with both shape and size in mind.
2. Material Selection
Material selection for gable windows is a critical aspect of building design, influencing durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic integration. The chosen materials must withstand environmental stressors while contributing to the overall architectural harmony of the structure.
Suggested read: Pro High Rise Window Cleaning | Sparkling Windows
-
Frame Material: Wood, Vinyl, Aluminum
Frame materials provide structural support and contribute significantly to thermal performance. Wood offers classic aesthetics but requires regular maintenance to prevent rot and insect infestation. Vinyl is a low-maintenance option with good insulation properties but may lack the aesthetic appeal of wood. Aluminum offers strength and durability, particularly in harsh climates, but is a poor insulator and can contribute to thermal bridging. The material choice must balance these factors, considering climate, budget, and desired aesthetic.
-
Glazing: Single, Double, and Triple Pane Options
Glazing impacts energy efficiency and noise reduction. Single-pane glass offers minimal insulation. Double-pane glazing with an inert gas fill significantly improves thermal performance by reducing heat transfer. Triple-pane glazing offers the highest level of insulation and noise reduction, but at a greater cost. Coatings, such as low-emissivity (low-E) coatings, further enhance energy efficiency by reflecting radiant heat. The choice of glazing depends on the desired level of energy efficiency and the climate zone.
-
Weather Stripping and Sealants
Weather stripping and sealants are essential for preventing air and water infiltration around the window frame. High-quality weather stripping, made from materials like EPDM rubber or silicone, provides a durable and effective seal. Sealants, such as silicone or polyurethane caulk, fill gaps between the window frame and the surrounding wall, preventing moisture damage and air leaks. Proper installation and maintenance of these materials are crucial for maintaining energy efficiency and preventing structural damage.
-
Fasteners and Hardware
The fasteners and hardware used to install gable windows must be corrosion-resistant and structurally sound. Stainless steel or coated fasteners are recommended to prevent rust and degradation, especially in coastal or humid environments. Hinges, locks, and handles should be durable and easy to operate. The choice of hardware should complement the overall design of the window and the architectural style of the building. Properly chosen and installed fasteners and hardware ensure the long-term stability and functionality of the gable window.
In summary, the selection of materials for a gable window demands a holistic consideration of structural requirements, aesthetic preferences, and environmental factors. The choices made directly impact the window’s longevity, performance, and contribution to the overall building design. A balance between cost, durability, and energy efficiency is essential for making informed decisions.
3. Structural Integration
The proper structural integration of a gable window is paramount to the overall stability and longevity of a building. The opening created within the gable end inherently weakens the structural integrity of the wall, necessitating careful design and execution to redistribute loads and maintain stability. Failure to adequately address structural considerations can lead to compromised weather resistance, premature deterioration of the surrounding wall, and potentially catastrophic structural failure.
-
Load Transfer Mechanisms
A primary function of structural integration is to ensure effective load transfer around the window opening. The gable wall, typically a load-bearing component, relies on continuous vertical members to transmit weight from the roof to the foundation. A window interrupts this continuity. Reinforcement strategies, such as headers and trimmer studs, are employed to redirect loads around the opening. For example, a large window requires a substantial header, often engineered lumber or steel, to span the opening and support the weight above. Inadequate headers can result in sagging of the roofline and cracking of the surrounding wall surfaces.
-
Shear Resistance
Shear forces, particularly those generated by wind loads or seismic activity, exert significant stress on gable walls. A window opening reduces the wall’s ability to resist these forces. Structural integration addresses this vulnerability through the use of sheathing materials, such as plywood or oriented strand board (OSB), which are fastened to the framing members. These sheathing panels provide lateral support and prevent racking of the wall. The nailing pattern and fastener type are critical for achieving the required shear resistance. A common example is the use of closer nail spacing around window openings to enhance shear capacity in high-wind zones.
-
Water Management
Effective water management is integral to structural longevity. Water infiltration around a gable window can lead to rot, mold growth, and corrosion of structural members. Proper integration involves the use of flashing materials, such as metal or flexible membranes, to divert water away from the window opening. Flashing is typically installed at the head, jambs, and sill of the window. An example is step flashing, which is interwoven with roofing shingles to provide a continuous barrier against water intrusion. Neglecting proper flashing can result in significant structural damage over time.
-
Connection Details
The connection between the window frame and the surrounding wall is a critical point of vulnerability. These connections must be robust enough to withstand wind loads and thermal expansion/contraction. Proper connection details include the use of appropriate fasteners, shims, and sealants. Fasteners should be corrosion-resistant and of sufficient length to penetrate the framing members. Shims are used to ensure a level and plumb installation, preventing stress on the window frame. Sealants, such as silicone or polyurethane caulk, prevent air and water infiltration. An example is the use of expanding foam insulation around the window perimeter to provide both insulation and structural support.
In conclusion, structural integration of a gable window is a multifaceted process requiring a comprehensive understanding of load transfer, shear resistance, water management, and connection details. Failure to adequately address these aspects can have significant consequences for the structural integrity and long-term performance of the building. Consulting with a qualified structural engineer or experienced contractor is essential to ensure that gable windows are properly integrated into the overall building structure, maintaining its stability and protecting it from the elements.
4. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency represents a critical consideration in modern building design, and gable windows present a unique challenge and opportunity in this context. Their location, typically high in the structure, exposes them to significant temperature fluctuations and solar radiation, directly influencing heating and cooling loads within the building. Optimizing the energy performance of these windows is therefore essential for minimizing energy consumption and maximizing occupant comfort.
-
Glazing Selection and Thermal Performance
The choice of glazing significantly impacts the thermal performance of a gable window. Single-pane glass offers minimal insulation, leading to substantial heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Double- or triple-pane windows, filled with inert gases such as argon or krypton, drastically reduce heat transfer. Low-emissivity (low-E) coatings further enhance energy efficiency by reflecting radiant heat. For example, a home in a cold climate would benefit from low-E coatings designed to reflect heat back into the building, while a home in a hot climate would benefit from coatings that reflect solar heat away from the building. The U-factor, a measure of heat transfer, should be as low as possible to minimize energy loss.
-
Air Leakage and Infiltration
Air leakage around the window frame can negate the benefits of high-performance glazing. Proper installation techniques, including the use of high-quality weather stripping and sealants, are crucial for minimizing air infiltration. Air leakage can also contribute to moisture problems, leading to mold growth and structural damage. Regular inspection and maintenance of weather stripping and sealants are necessary to maintain energy efficiency. For instance, caulking can dry out and crack over time, creating pathways for air and water to enter the building. Addressing air leakage is essential for maximizing the energy performance of gable windows.
Suggested read: Professional Window Tinting Service - Quality Windows
-
Window Orientation and Shading
The orientation of the gable window relative to the sun significantly impacts its energy performance. South-facing windows receive the most direct sunlight, potentially leading to overheating in summer. East- and west-facing windows also experience significant solar gain during specific times of the day. Shading devices, such as awnings, overhangs, or trees, can mitigate solar heat gain, reducing cooling loads. Window films can also be applied to reduce solar radiation. In contrast, passive solar heating strategies can utilize south-facing windows to capture solar heat in winter, reducing heating costs. Careful consideration of window orientation and shading is crucial for optimizing energy performance.
-
Frame Material and Insulation
The frame material of a gable window also contributes to its overall energy efficiency. Wood and vinyl frames offer better insulation than aluminum frames, which are highly conductive. Thermal breaks, incorporated into aluminum frames, can reduce heat transfer. Insulating the space around the window frame is also important for preventing thermal bridging. Expanding foam insulation can fill gaps and create an airtight seal. The R-value, a measure of thermal resistance, should be as high as possible to minimize heat loss. Selecting a frame material with good insulation properties and ensuring proper installation are essential for maximizing energy efficiency.
In conclusion, achieving optimal energy efficiency in gable windows necessitates a comprehensive approach encompassing glazing selection, air leakage control, consideration of window orientation and shading, and the choice of appropriate frame materials and insulation. By addressing these factors, building designers and homeowners can significantly reduce energy consumption and create more comfortable and sustainable living environments.
5. Aesthetic Impact
The integration of gable windows into architectural designs significantly influences a building’s aesthetic presence. The selection, placement, and style of these windows contribute to the overall visual appeal and character of a structure.
-
Architectural Style Harmony
Gable windows must align with the prevailing architectural style to maintain aesthetic cohesion. A Victorian-era home, for example, may feature ornate, arched gable windows with decorative trim. Conversely, a modern home might incorporate minimalist, rectangular windows with clean lines. The design of the window should complement the roof pitch, siding material, and overall design language of the building. A mismatch in style can detract from the building’s visual appeal and create a sense of disharmony.
-
Proportion and Balance
The size and placement of gable windows must be proportional to the overall facade of the building. Overly large windows can overwhelm the gable end, while windows that are too small may appear insignificant. Symmetry and balance are crucial considerations. Centrally located windows create a sense of stability, while asymmetrical arrangements can introduce visual interest and dynamism. However, asymmetrical designs must be carefully executed to avoid appearing haphazard or unbalanced. The size and placement must complement the scale of the building and the surrounding architectural elements.
-
Material and Finish
The materials and finishes used in gable windows significantly impact their aesthetic contribution. Wood frames offer a traditional, warm aesthetic, while metal frames provide a more modern, industrial look. The color and texture of the frame should harmonize with the siding and roofing materials. Glazing options, such as tinted or patterned glass, can further enhance the aesthetic appeal. The choice of materials and finishes must consider the building’s overall color palette and design aesthetic. Harmonious material choices contribute to a cohesive and visually pleasing exterior.
-
Light and Shadow
Gable windows play a critical role in shaping the interplay of light and shadow on the building’s facade. The size, shape, and placement of the window influence the amount of natural light that enters the attic space or upper floors, creating interior ambiance. Exterior lighting schemes can accentuate the window’s architectural details, creating visual interest at night. The interplay of light and shadow can highlight the window’s form and texture, adding depth and dimension to the building’s overall aesthetic. Careful consideration of light and shadow enhances the building’s visual appeal and creates a dynamic, engaging facade.
In conclusion, the aesthetic impact of gable windows is a multifaceted consideration encompassing architectural style, proportion, material choices, and the interplay of light. Thoughtful design and integration of these elements result in a visually appealing building that enhances its surrounding environment. A well-executed gable window design adds character and visual interest, significantly contributing to the building’s overall aesthetic value.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gable Windows
This section addresses common inquiries regarding gable windows, offering concise and factual responses to enhance understanding of their design, function, and maintenance.
Question 1: What is the primary purpose of a gable window?
A gable window serves to provide natural light and ventilation to attic spaces or rooms situated beneath a pitched roof. It enhances interior illumination while facilitating air circulation within the structure.
Question 2: What are the common shapes and sizes available for gable windows?
Gable windows are typically available in rectangular, arched, or triangular shapes, dependent upon the architectural design and structural limitations of the gable end. Size is constrained by the dimensions of the gable and load-bearing requirements.
Question 3: What materials are typically used for gable window frames?
Common frame materials include wood, vinyl, and aluminum. Wood provides aesthetic appeal but requires maintenance. Vinyl offers durability and low maintenance, while aluminum provides strength but is a less effective insulator.
Question 4: How does a gable window impact the energy efficiency of a building?
Gable windows can influence energy efficiency. High-performance glazing, proper sealing, and appropriate shading can minimize heat transfer and air leakage, reducing heating and cooling costs. The window’s orientation relative to sunlight also plays a role.
Question 5: What structural considerations are necessary when installing a gable window?
Structural integration is crucial. Headers and trimmer studs are required to redistribute loads around the window opening. Shear resistance and water management are also essential to prevent structural damage from wind and moisture.
Question 6: How often should gable windows be inspected and maintained?
Gable windows should be inspected annually for signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or deterioration of the frame or glazing. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and resealing, prolongs the lifespan of the window and preserves its functionality.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of gable windows ensures informed decisions regarding their selection, installation, and upkeep, optimizing their contribution to building design and performance.
The next section will provide guidance on selecting appropriate gable window styles for various architectural designs, offering practical advice for enhancing the aesthetic appeal of a structure.
Gable Window Installation and Maintenance Tips
This section provides essential recommendations for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of this architectural element. Careful attention to these guidelines will help maintain structural integrity, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal.
Tip 1: Proper Framing is Paramount. Prior to installation, ensure the gable wall framing is square and plumb. Deviations can lead to improper window fit, compromising weather sealing and structural stability. Verify header dimensions are sufficient to support the load above, consulting with a structural engineer if necessary.
Tip 2: Employ Appropriate Flashing Techniques. Effective flashing is critical for preventing water infiltration. Use step flashing at the sides, integrating it with the roofing material. Overlap flashing adequately to channel water away from the window opening. Utilize a continuous head flashing to divert water above the window.
Tip 3: Select High-Quality Sealants. Choose sealants specifically designed for exterior use, exhibiting UV resistance and flexibility. Apply sealant liberally to all gaps between the window frame and the wall sheathing. Ensure proper adhesion by cleaning surfaces thoroughly before application. Regularly inspect and replace sealant as needed to maintain a weather-tight seal.
Suggested read: Protect: Window Well Liners - Easy Install!
Tip 4: Consider Glazing Options for Energy Efficiency. Select glazing options appropriate for the climate. Low-E coatings reduce heat transfer, while gas fills (argon or krypton) enhance insulation. Double or triple-pane windows provide superior thermal performance compared to single-pane options. Consider window orientation when selecting glazing types to optimize energy savings.
Tip 5: Prioritize Proper Fastener Selection. Utilize corrosion-resistant fasteners, such as stainless steel or coated screws, to secure the window frame to the wall framing. Employ fasteners of adequate length to penetrate framing members securely. Avoid over-tightening, which can distort the window frame and compromise sealing.
Tip 6: Inspect and Maintain Regularly. Conduct annual inspections of the window frame, glazing, and sealant. Address any signs of damage promptly, such as cracks, leaks, or deterioration. Clean the window regularly to remove dirt and debris, which can impede visibility and contribute to material degradation.
Adhering to these guidelines will contribute to the long-term performance and value of the installation. Proper attention to detail during installation and consistent maintenance practices are essential for maximizing the benefits and minimizing potential issues.
The concluding section will summarize the key advantages of gable windows and their significance in architectural design.
Conclusion
This article explored various facets of gable windows, emphasizing their role in architectural design and structural integrity. The discussion encompassed design considerations such as shape, size, material selection, and energy efficiency, alongside the critical importance of structural integration and aesthetic harmony. Proper installation and maintenance practices were also outlined, underscoring the need for adherence to industry standards for long-term performance.
The effective utilization of the gable window requires careful consideration of both functional and aesthetic requirements. Implementing best practices ensures structural stability, enhances energy conservation, and contributes to the overall architectural value of a building. Continued research and development in window technology are likely to further improve the performance and design possibilities of this enduring architectural element, prompting further exploration of its capabilities and applications.




![Download Toki Pona Language Pack for Windows - [Updated] 19 download toki pona language pack for windows updated](https://superagc.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/download-toki-pona-language-pack-for-windows-updated.webp)